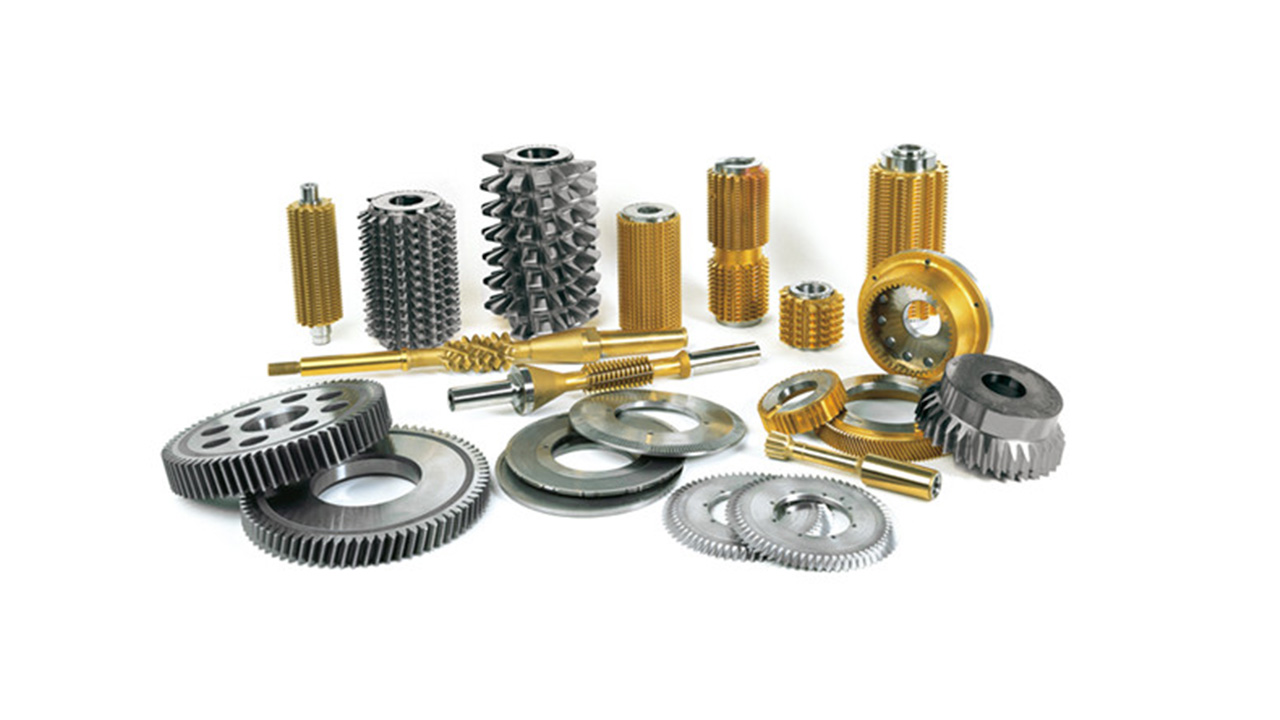
In essence, PVD hard coatings are the technology of choice wherever a component is subject to mechanical wear, chemical attack, high temperatures, or requires a combination of durability and aesthetic appeal. Their ability to dramatically extend service life, improve performance, and enable new design possibilities makes them indispensable across advanced manufacturing, transportation, luxury goods, and medical industries.
Advantages of PVD Technology for Hard Coatings:
-
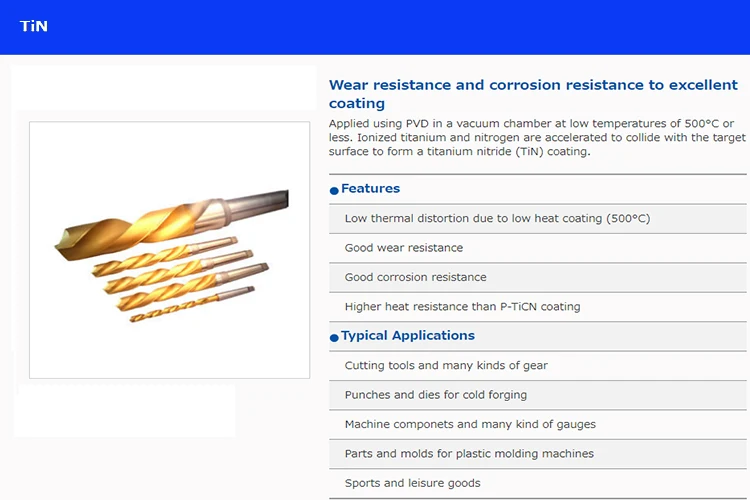
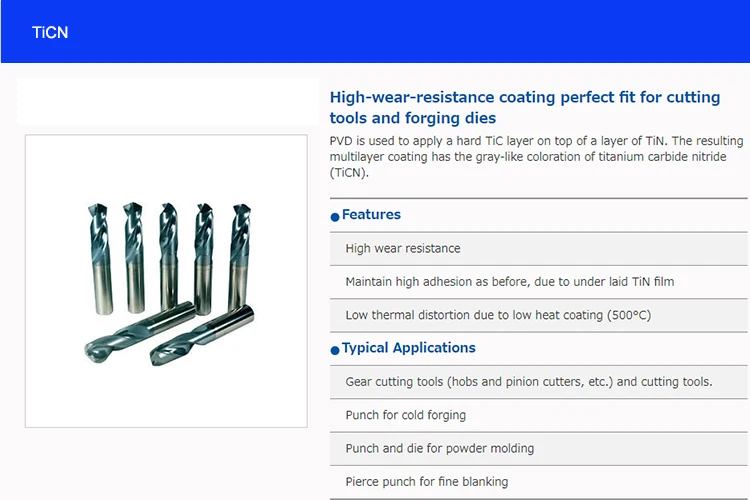
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance: PVD coatings, such as TiN, TiAlN, CrN, and DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon), are extremely hard (often exceeding 2000 HV). This significantly enhances the surface hardness of tools, molds, and components, providing superior resistance to abrasion, erosion, and wear, thereby extending service life.
-
Low Coefficient of Friction: Many PVD coatings have naturally lubricious properties. This reduces friction between contacting surfaces, leading to lower energy consumption, less heat generation, improved efficiency, and reduced galling or seizing in moving parts.
-
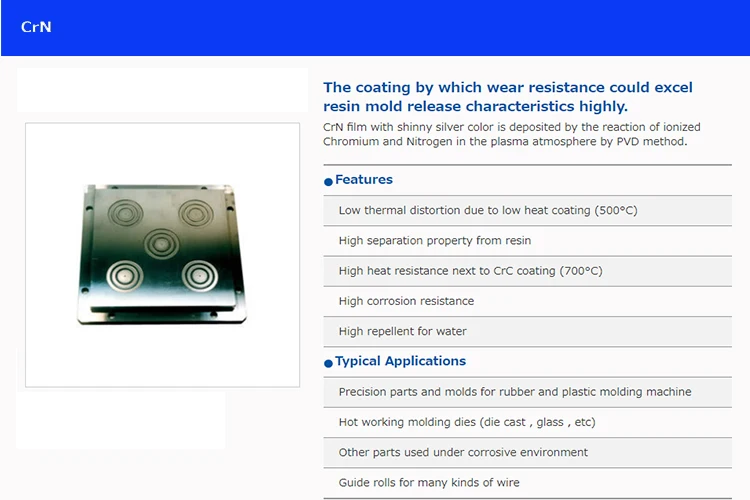
Excellent Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance: The dense, non-porous structure of PVD coatings acts as a highly effective barrier against environmental factors. It protects the substrate from corrosion (e.g., from coolants or chemicals) and high-temperature oxidation, which is crucial for tools used in demanding environments.
-
High Temperature Stability: Certain PVD coatings (e.g., TiAlN) form a stable, protective oxide layer at high temperatures (often above 800°C). This allows them to maintain their properties in high-speed machining or dry cutting applications where temperatures soar.
-
Superb Adhesion to Substrates: The PVD process, especially techniques like cathodic arc evaporation or unbalanced magnetron sputtering, involves high-energy ion bombardment. This cleans and activates the substrate surface, creating a very strong metallurgical bond between the coating and the substrate, preventing flaking or delamination under stress.
-
Precise and Uniform Coating Thickness: PVD allows for extremely precise control over coating thickness (typically in the range of 1 to 5 microns). The coating is applied uniformly, even on complex geometries with sharp edges or deep grooves, ensuring consistent performance across the entire part.
-
No Thermal Distortion of the Substrate: Unlike some Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes, PVD is carried out at relatively low temperatures (typically 200°C - 500°C). This prevents annealing, distortion, or loss of hardness in precision-engineered substrates, such as hardened tool steels.
-
Excellent Surface Finish and Aesthetic Versatility: PVD can produce surfaces with very low roughness, mirroring the substrate's finish. It is also widely used for decorative applications due to the availability of a wide range of attractive, durable colors (gold, bronze, black, blue, etc.) that are highly scratch-resistant.
-
Environmentally Friendly Process ("Green Technology"): PVD is a dry, vacuum-based process. It generates no hazardous wet chemicals or toxic gases, and it produces minimal waste, making it a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to many traditional plating processes.
-
Material and Design Flexibility: A vast variety of pure metals, alloys, nitrides, carbides, and oxides can be deposited using PVD. Furthermore, modern systems allow for the deposition of advanced multilayer, nanocomposite, or gradient coatings tailored for specific extreme applications.
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) hard coatings are ideally suited for a wide range of applications where surface properties need to be enhanced.
1. Cutting & Machining Tools
-
Applications: Drills, end mills, inserts, milling cutters, taps, reamers, saw blades, gear cutters.
-
Why PVD? Coatings like TiAlN, AlCrN, and TiSiN provide extreme surface hardness, reduce friction, and resist high-temperature oxidation. This significantly increases tool life (often by 3-10x), allows for higher cutting speeds, enables dry or near-dry machining, and improves surface finish on the workpiece.
2. Molding & Forming Tools
-
Applications: Injection molds, die-casting molds, stamping dies, forging dies, extrusion tools.
-
Why PVD? Coatings such as CrN, TiCN, and DLC offer excellent wear resistance against abrasive plastics or metals, prevent galling and material adhesion (anti-stick properties), and enhance corrosion resistance from release agents or molten materials. This reduces downtime for cleaning and polishing, extends mold life, and improves part quality.
3. Wear Parts & Automotive Components
-
Applications: Engine components (piston rings, pins, tappets), transmission parts, fuel injectors, hydraulic components, bearings, pump parts.
-
Why PVD? Coatings like CrN, DLC, and WC/C provide a hard, low-friction surface that reduces wear, minimizes energy loss due to friction, and resists corrosion from fuels and lubricants. This leads to improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and longer component lifespan.
4. Decorative & Functional Finishes
-
Applications: Watch cases/bracelets, eyewear frames, jewelry, bathroom fixtures, automotive trim, consumer electronics.
-
Why PVD? It provides an extremely durable, scratch-resistant, and tarnish-resistant layer in various colors (gold, rose gold, black, blue, gunmetal). The process is environmentally friendly compared to traditional electroplating and offers superior adhesion and longevity.
5. Aerospace & High-Tech Components
-
Applications: Turbine blades, compressor parts, aerospace fasteners, satellite components.
-
Why PVD? Coatings such as TiAlN, AlTiN, and specialized thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) protect against extreme temperatures, oxidation, hot corrosion, and fretting wear. They are critical for performance and reliability in demanding environments.
6. Medical Devices & Surgical Tools
-
Applications: Surgical blades, orthopedic implants (knees, hips), dental drills and implants, endoscopic instruments.
-
Why PVD? Biocompatible coatings like TiN, ZrN, and DLC enhance surface hardness, provide excellent corrosion resistance against bodily fluids, and reduce friction. On implants, they can improve osseointegration (bone bonding). On tools, they increase sharpness retention and allow for easier cleaning/sterilization.
7. Precision Components for General Industry
-
Applications: Gears, shafts, seals, valves, slitters, textile guides, optical molds.
-
Why PVD? The technology is used to solve specific problems of wear, friction, and corrosion on critical precision parts, thereby reducing maintenance costs, improving process reliability, and extending the service intervals of machinery.

